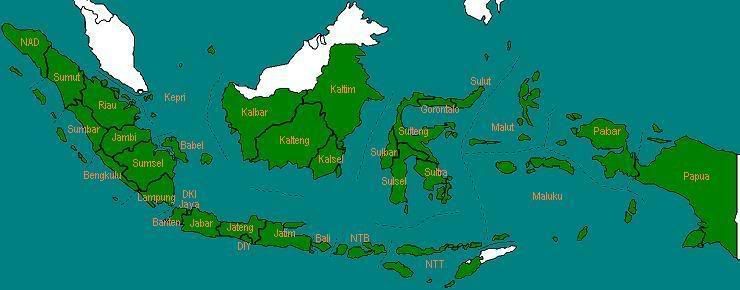
Pada tahun 1945, pemerintah menetapkan Indonesia dibagi menjadi delapan provinsi, yaitu Sumatera, Jawa Barat, Jawa Tengah, Jawa Timur, Borneo, Sulawesi, Sunda Kecil, dan Maluku.
Jumlah provinsi: 8
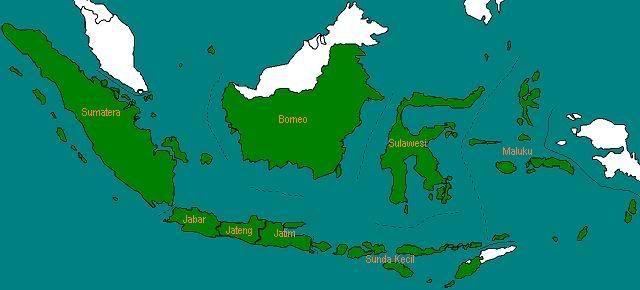
Antara tahun 1946-1949, terdapat berbagai perubahan perubahan wilayah Indonesia karena munculnya negara-negara baru dalam wilayah Indonesia.
Pada akhir tahun 1949, ketika Belanda mengakui kemerdekaan RIS (Republik Indonesia Serikat), RIS terdiri atas 16 negara bagian dan 1 Wilayah Federal Batavia.
Keenam belas negara bagian itu antara lain: Republik Indonesia, Negara Sumatera Timur, Riau, Negara Sumatera Selatan, Bangka, Belitung, Negara Pasundan, Jawa Tengah, Negara Jawa Timur, Negara Madura, Daerah Istimewa Borneo Barat, Dayak Besar, Federasi Borneo Timur, Daerah Banjar, Borneo Tenggara, dan Negara Indonesia Timur.

Pada awal tahun 1950, muncul gerakan untuk kembali ke negara kesatuan. Akibatnya tiap-tiap negara bagian mulai menyatukan diri satu per satu dengan Republik Indonesia.
Awal Agustus 1950, RIS hanya terdiri atas 4 negara bagian, yaitu Republik Indonesia, Negara Sumatera Timur, Daerah Istimewa Borneo Barat, dan Negara Indonesia Timur.
Dan pada tanggal 17 Agustus 1950, RIS dinyatakan bubar dan diganti dengan NKRI, dan ketiga negara bagian selain RI dinyatakan bubar dan dimasukkan ke dalam wilayah NKRI.
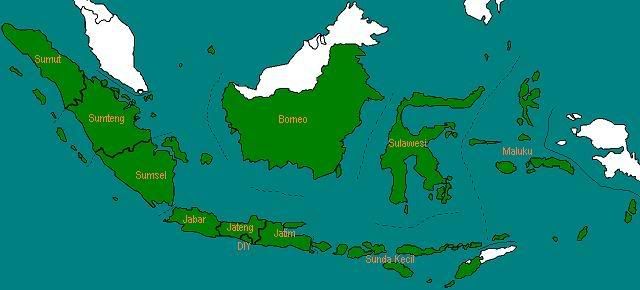
Pada tahun 1950, Yogyakarta dikeluarkan dari Jawa Tengah menjadi provinsi tersendiri dan diberi status Daerah Istimewa, dengan nama Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta. Pada tahun yang sama, Provinsi Sumatera dipecah menjadi tiga provinsi, yaitu Sumatera Utara, Sumatera Tengah, dan Sumatera Selatan.
Jumlah provinsi: 11
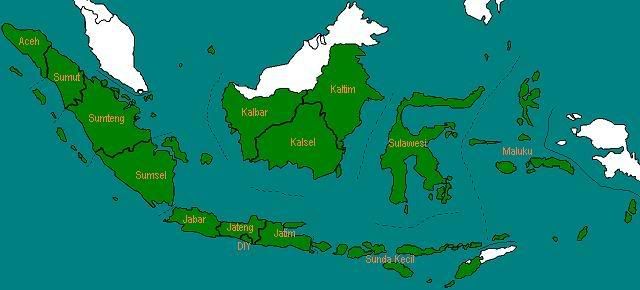
Pada tahun 1953, Provinsi Borneo diganti namanya menjadi Kalimantan.
Pada tahun 1956, Provinsi Aceh terbentuk, hasil pemekaran dari Sumatera Utara. Dan di akhir tahun 1956, Kalimantan dipecah menjadi tiga provinsi, yaitu Kalimantan Barat, Kalimantan Selatan, dan Kalimantan Timur.
Jumlah provinsi: 14
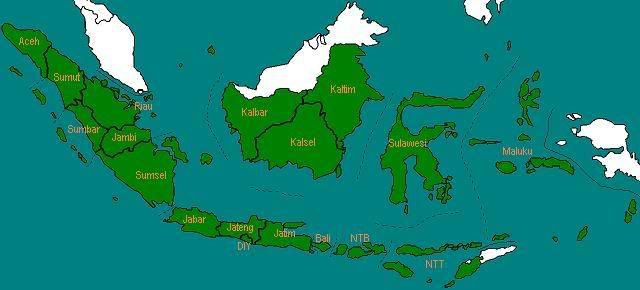
Pada tahun 1958, Provinsi Sumatera Tengah dipecah menjadi tiga provinsi, yaitu Sumatera Barat, Riau, dan Jambi. Kemudian Provinsi Sunda Kecil juga dipecah menjadi tiga provinsi, yaitu Bali, Nusa Tenggara Barat, dan Nusa Tenggara Timur.
Jumlah provinsi: 18
Pada tahun 1959, Provinsi Kalimantan Tengah terbentuk, hasil pemekaran dari Kalimantan Selatan. Dan pada akhir tahun 1959, Provinsi Aceh diberi status Daerah Istimewa, dengan nama Daerah Istimewa Aceh.
Jumlah provinsi: 19
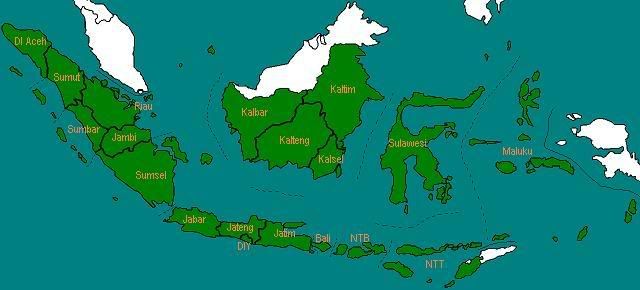
Pada tahun 1960, Provinsi Sulawesi dipecah menjadi dua provinsi, yaitu Sulawesi Utara dan Sulawesi Selatan.
Jumlah provinsi: 20
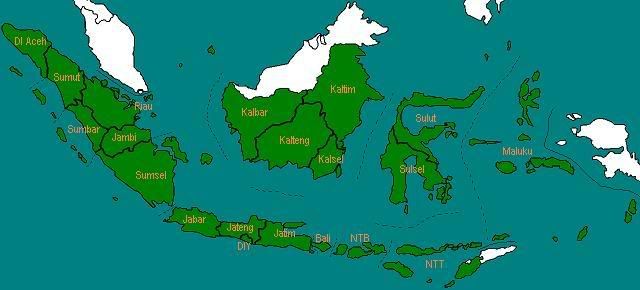
Pada tahun 1961, Kota Jakarta resmi dikeluarkan dari Jawa Barat dan menjadi provinsi tersendiri dan diberi status Daerah Khusus Ibukota, dengan nama Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta Raya.
Jumlah provinsi: 21
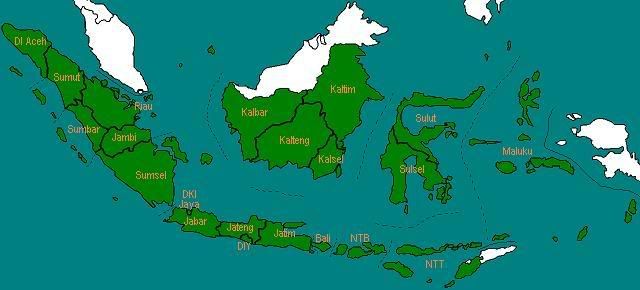
Pada tahun 1963, PBB (Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa) menyerahkan administrasi wilayah Irian Barat kepada Indonesia.
Pada tahun 1964, tiga provinsi baru terbentuk, yaitu Lampung (dari Sumatera Selatan), Sulawesi Tengah (dari Sulawesi Utara), dan Sulawesi Tenggara (dari Sulawesi Selatan). Kemudian, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta Raya secara resmi ditetapkan sebagai ibukota Republik Indonesia.
Jumlah provinsi: 24
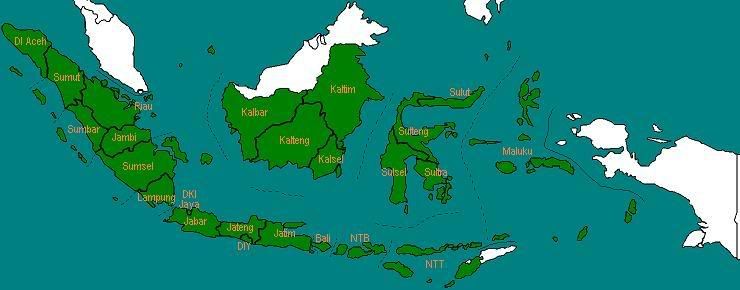
Pada tahun 1968, Provinsi Bengkulu terbentuk, hasil pemekaran dari Sumatera Selatan.
Jumlah provinsi: 25
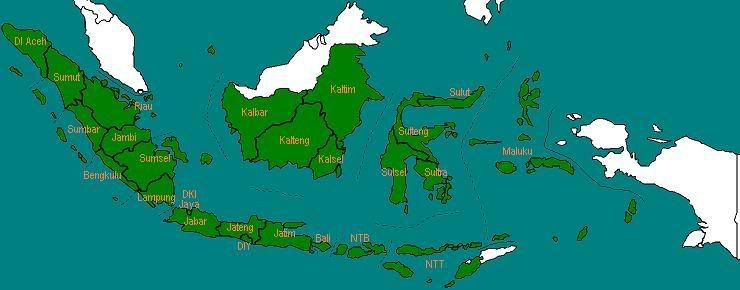
Pada tahun 1969, setelah diadakan Pepera (Penentuan Pendapat Rakyat), Irian Barat secara resmi menjadi bagian dari NKRI dan menjadi salah satu provinsi di Indonesia.
Jumlah provinsi: 26
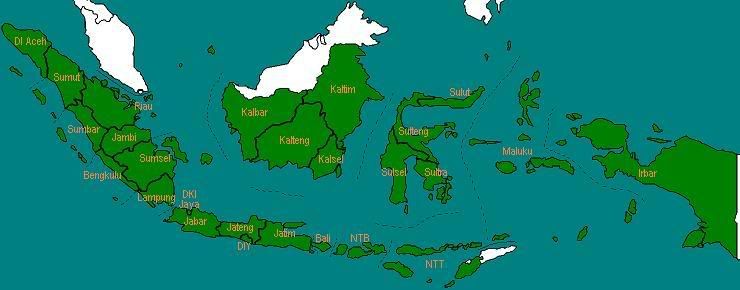
Pada tahun 1973, Provinsi Irian Barat diubah namanya menjadi Irian Jaya.
Pada akhir tahun 1975, Indonesia menguasai wilayah Timor Timur.
Pada tahun 1976, Timor Timur dimasukkan ke dalam wilayah NKRI dan menjadi salah satu provinsi di Indonesia.
Jumlah provinsi: 27
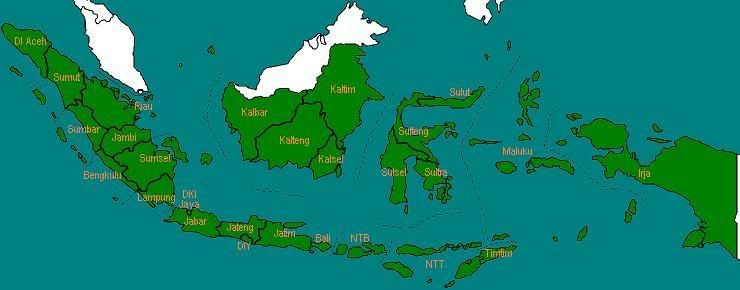
Pada tahun 1999, diadakan jajak pendapat (referendum) di Timor Timur dan Timor Timur secara resmi keluar dari NKRI. Dan di akhir tahun 1999, Provinsi Maluku Utara terbentuk, hasil pemekaran dari Provinsi Maluku.
Jumlah provinsi: 27
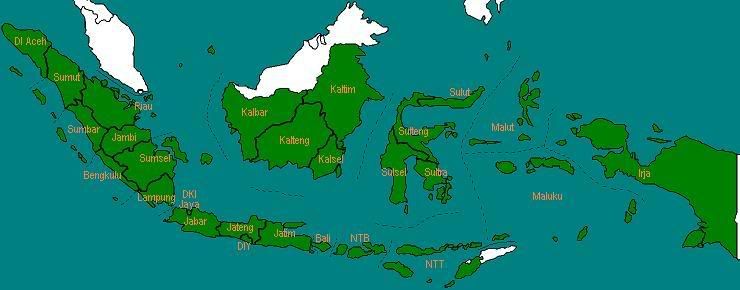
Pada awal tahun 2000, Provinsi Irian Jaya diganti namanya menjadi Papua. Kemudian pada akhir tahun 2000, Provinsi Banten resmi berdiri, dimekarkan dari Jawa Barat.
Jumlah provinsi: 28
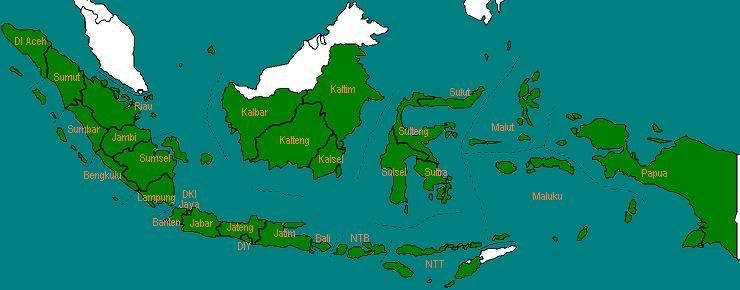
Pada tahun 2001, dua provinsi baru resmi berdiri, yaitu Kepulauan Bangka Belitung (dari Sumatera Selatan) dan Gorontalo (dari Sulawesi Utara). Pada tahun yang sama, Daerah Istimewa Aceh diganti namanya menjadi Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam, dan diberi status Otonomi Khusus. Sama halnya dengan NAD, Provinsi Papua juga diberi status Otonomi Khusus.
Jumlah provinsi: 30
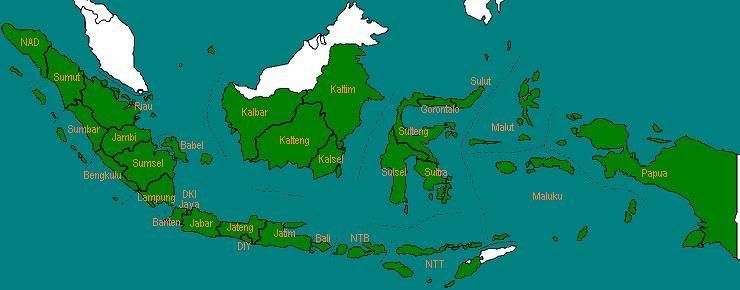
Pada tahun 2003, Provinsi Irian Jaya Barat resmi berdiri, hasil pemekaran dari Provinsi Papua.
Jumlah provinsi: 31
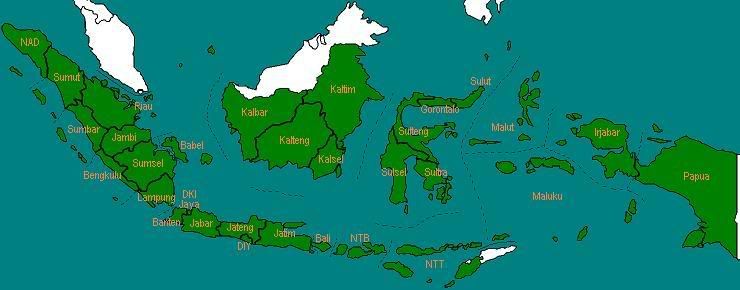
Pada tahun 2004, dua provinsi baru resmi berdiri, yaitu Kepulauan Riau (dari Provinsi Riau) dan Sulawesi Barat (dari Sulawesi Selatan).
Jumlah provinsi: 33
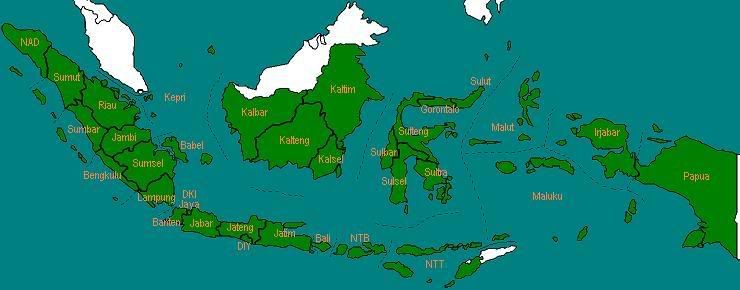
Pada tahun 2007, Provinsi Irian Jaya Barat diubah namanya menjadi Papua Barat.





































 Rumbai Stadium will be a multi-use stadium in Pekanbaru, Riau, Indonesia. The stadium will holds 70,000 people. It still building and will finish in 2010. The stadium will be the main venue for the 2012 National Games and projected to host 2018-2022 FIFA World Cup.
Rumbai Stadium will be a multi-use stadium in Pekanbaru, Riau, Indonesia. The stadium will holds 70,000 people. It still building and will finish in 2010. The stadium will be the main venue for the 2012 National Games and projected to host 2018-2022 FIFA World Cup.



















